322. Coin Change
You are given coins of different denominations and a total amount of money amount. Write a function to compute the fewest number of coins that you need to make up that amount. If that amount of money cannot be made up by any combination of the coins, return -1.
Example 1:
Input: coins = [1, 2, 5], amount = 11
Output: 3
Explanation: 11 = 5 + 5 + 1
Example 2:
Input: coins = [2], amount = 3
Output: -1
Note:
You may assume that you have an infinite number of each kind of coin.
题解思路1 贪心(WA)
看到本题,感觉和 leetcode 39. Combination Summ 这题比较相似,都是求满足和为某个target的序列,不过本题没有要求输出所有序列的集合,而是要输出所用数字最少序列的size。
我的第一个想法是贪心
- 将输入数组排序
- 每次都取可能的最大的数,去拼凑amount
- 找出第一个满足和为amount的序列,该序列的大小即为所求
事实证明,贪心法是不正确的,比如,对于
Input: coins = [5, 4, 1], amount = 18
Output: 6
Explanation: 18 = 5 + 5 + 5 + 1 + 1 + 1
可事实上,正确的最优解,应该是:
Input: coins = [5, 4, 1], amount = 18
Output: 4
Explanation: 18 = 5 + 5 + 4 + 4
贪心算法结果:WA
题解思路2 DFS暴力搜索(TLE)
既然贪心算法不正确,那就按 leetcode 39. Combination Summ 的解法一样,把所有可能的结果都搜索出来,同时根据每个满足条件的搜索结果,更新最终解,思路应该是正确的,但这种暴力的算法,显然会Time Limit Exceed。
code
class Solution {
public:
void dfs(vector<int>& coins, int cap, int& res, int cur, int start)
{
if (cap == 0) {
res = min(res, cur);
return;
}
if (cap < 0) return;
for (int i = start; i < coins.size(); ++i) {
dfs(coins, cap - coins[i], res, cur + 1, i);
}
}
int coinChange(vector<int>& coins, int amount) {
if (coins.empty()) return -1;
sort(coins.rbegin(), coins.rend());
int res = INT_MAX;
dfs(coins, amount, res, 0, 0);
return res == INT_MAX ? -1 : res;
}
};
题解思路3 DFS + memo 备忘录(AC)
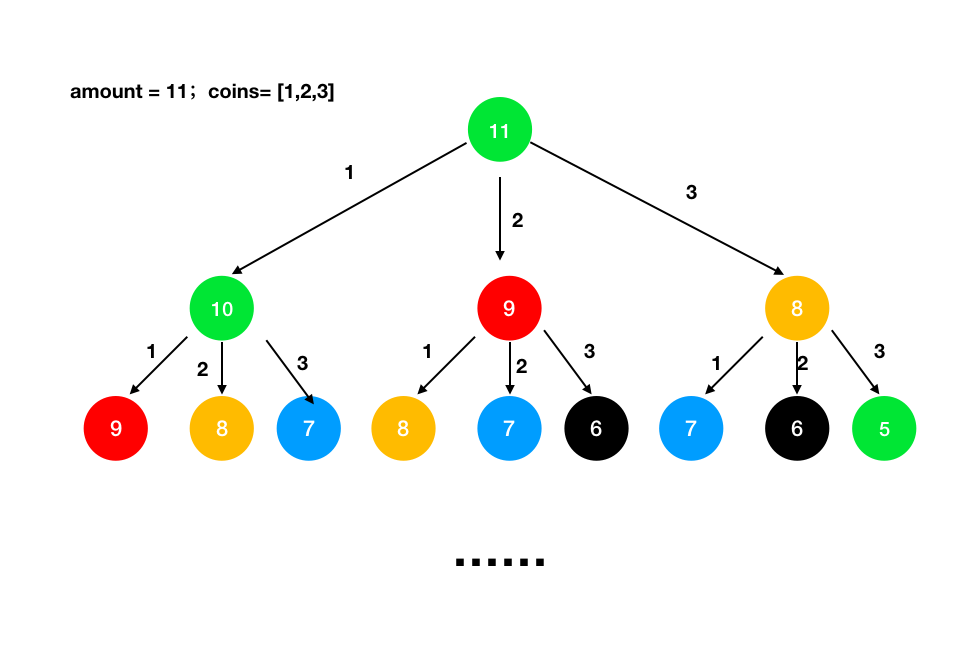
之所以DFS会超时,是因为我们在进行递归搜索时,处理了太多重复的分支。为此,我们可以使用备忘录法,将搜索出的部分结果先存起来,以备下次使用。
开一个大小为amount + 1的数组memo,memo[i]则表示了目标为i时,我们需要的最少方案。那么memo[amout],显然为我们的最终目标解。
定义
// @coins 输入数组
// @target 当前搜索目标
// @memo 备忘录
// return 目标为target时,所需的最少的硬币个数
int dfs(vector<int>& coins, int target, vector<int>& memo)
依然dfs, target为amount
1. 如果发现memo[target]存在,直接使用结果。(递归收敛)
2. 遍历所有硬币,递归去搜索 target - coins[i],根据递归返回结果更新memo
code
class Solution {
public:
int dfs(vector<int>& coins, int target, vector<int>& memo)
{
if (target < 0) return -1;
if (memo[target] != INT_MAX) return memo[target];
for (int i = 0; i < coins.size(); ++i) {
int t = dfs(coins, target - coins[i], memo);
if (t >= 0) memo[target] = min(memo[target], t + 1);
}
if (memo[target] == INT_MAX) memo[target] = -1;
return memo[target];
}
int coinChange(vector<int>& coins, int amount) {
if (coins.empty()) return -1;
vector<int> memo(amount + 1, INT_MAX);
memo[0] = 0;
return dfs(coins, amount, memo);
}
};
题解思路4 DP 动态规划(AC)
其实dfs+memo,就是一种自顶向下的DP,分析其过程,可以总结出递推方程:
dp[i] = 0, if i == 0
dp[i] = min(dp[i], dp[i - coins[j]] + 1), if 0 < i <= amount
根据递推方程,代码如下:
code
class Solution {
public:
int coinChange(vector<int>& coins, int amount) {
if (coins.empty()) return -1;
vector<int> dp(amount + 1, amount + 1);
dp[0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < dp.size(); ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < (int)coins.size(); ++j) {
if (i - coins[j] >= 0) dp[i] = min(dp[i], dp[i - coins[j]] + 1);
}
}
return dp[amount] > amount ? -1 : dp[amount];
}
};
注意:dp初始化时,不能初始化为INT_MAX,否则 dp[i - coins[j]] + 1 可能大于INT_MAX,造成int overflow


赞, 简单明了不怎么跳步骤…