题目描述
用以太网线缆将 n 台计算机连接成一个网络,计算机的编号从 0 到 n-1。线缆用 connections 表示,其中 connections[i] = [a, b] 连接了计算机 a 和 b。
网络中的任何一台计算机都可以通过网络直接或者间接访问同一个网络中其他任意一台计算机。
给你这个计算机网络的初始布线 connections,你可以拔开任意两台直连计算机之间的线缆,并用它连接一对未直连的计算机。请你计算并返回使所有计算机都连通所需的最少操作次数。如果不可能,则返回 -1。
样例
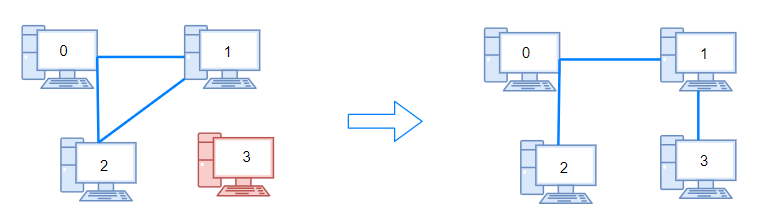
输入:n = 4, connections = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,2]]
输出:1
解释:拔下计算机 1 和 2 之间的线缆,并将它插到计算机 1 和 3 上。
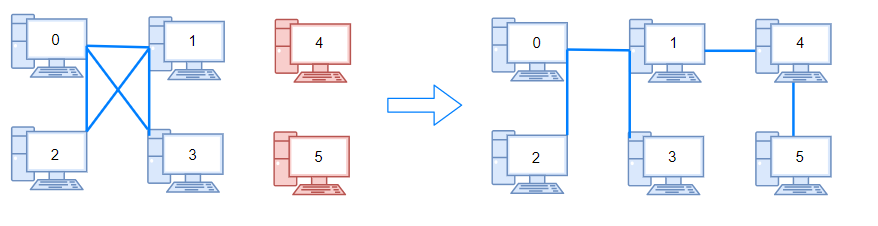
输入:n = 6, connections = [[0,1],[0,2],[0,3],[1,2],[1,3]]
输出:2
输入:n = 6, connections = [[0,1],[0,2],[0,3],[1,2]]
输出:-1
解释:线缆数量不足。
输入:n = 5, connections = [[0,1],[0,2],[3,4],[2,3]]
输出:0
限制
1 <= n <= 10^51 <= connections.length <= min(n*(n-1)/2, 10^5)connections[i].length == 20 <= connections[i][0], connections[i][1] < nconnections[i][0] != connections[i][1]- 没有重复的连接。
- 两台计算机不会通过多条线缆连接。
算法
(并查集) $O(n + m)$
- 如果当前线缆的个数小于
n - 1,则显然无法完成任务。 - 接下来根据当前线缆的连接情况求连通块的个数。这可以用带路径压缩和按大小合并的并查集实现。
- 最后,如果当前有
k个连通块,则答案就是k - 1。这是因为每接通一个连通块,都只需要一根线缆的移动(我们已经保证了线缆数目够用)。
时间复杂度
- 并查集操作的时间复杂度近似为常数,故总时间复杂度为 $O(n + m)$。其中 $m$ 为当前线缆的个数。
空间复杂度
- 需要额外 $O(n)$ 的空间来支持并查集。
C++ 代码
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> f, sz;
int find(int x) {
return x == f[x] ? x : f[x] = find(f[x]);
}
int makeConnected(int n, vector<vector<int>>& connections) {
if (connections.size() < n - 1)
return -1;
f.resize(n);
sz.resize(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
f[i] = i;
sz[i] = 1;
}
for (const auto &c : connections) {
int fx = find(c[0]);
int fy = find(c[1]);
if (fx != fy) {
if (sz[fx] < sz[fy]) {
f[fx] = fy;
sz[fy] += sz[fx];
} else {
f[fy] = fx;
sz[fx] += sz[fy];
}
}
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (find(i) == i)
ans++;
return ans - 1;
}
};

