树的遍历 + BFS
时间复杂度 $O(N)$
注意:
1、给定 前序、中序遍历,可求 后序、层序遍历。
2、给定 后序、中序遍历,可求 前序、层序遍历。
3、给定 前序、后序遍历,无法唯一确定 中序、层序遍历(因为有 前序和后序遍历 重复信息)。
已知 中序和后序遍历,求解 层序遍历。
思路:
我们需要利用 中序和后序遍历 建立一颗二叉树,对二叉树进行 BFS 即可,核心就在于如何建树。
中序遍历的顺序:左->根->右,后序遍历的顺序:左->右->根,先用哈希表将中序遍历的每个元素的位置记录下来,方便后续查找后序遍历的根在中序遍历中的位置,以此划分中序、后序当前根的左右子树,再不断的左、右递归建树。
示意图如下:
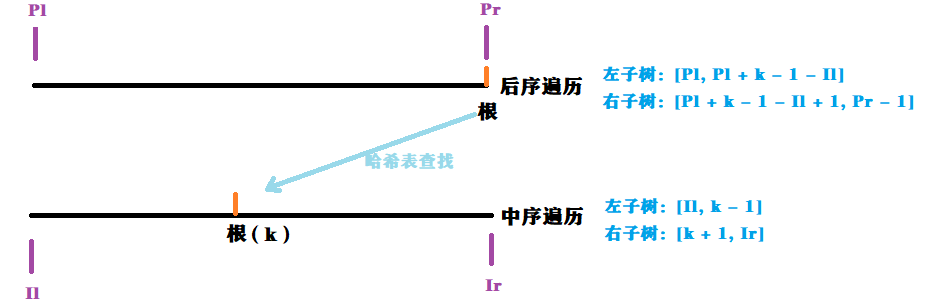
当树建好后,只需对得到的 L[]、R[] 进行 BFS 即可得到层序遍历。
因为每个节点只被遍历了一次,所以时间复杂度为 $O(N)$。
C++ 代码
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
const int N = 40;
int n;
int postorder[N], inorder[N];
unordered_map<int, int> l, r, pos;
// 后序遍历:左右根
// 中序遍历:左根右
int build(int il, int ir, int pl, int pr)
{
int root = postorder[pr];
int k = pos[root]; // 根节点在中序遍历中位置
if (il < k) l[root] = build(il, k - 1, pl, pl + k - 1 - il); // 左子树
if (ir > k) r[root] = build(k + 1, ir, pl + k - 1 - il + 1, pr - 1); // 右子树
return root;
}
void bfs(int root) // bfs 实现层序遍历
{
queue <int> q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
int t = q.front();
q.pop();
cout << t << ' ';
if (l[t]) q.push(l[t]);
if (r[t]) q.push(r[t]);
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) cin >> postorder[i];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
cin >> inorder[i];
pos[inorder[i]] = i; // 记录中序遍历中每个点的位置
}
int root = build(0, n - 1, 0, n - 1); // 重建 二叉树
bfs(root);
return 0;
}

