思路:后序遍历根节点在最后一个,前序遍历根节点是第一个,根据根节点位置在中序遍历中可以区分出左右子树,据此来重建二叉树。
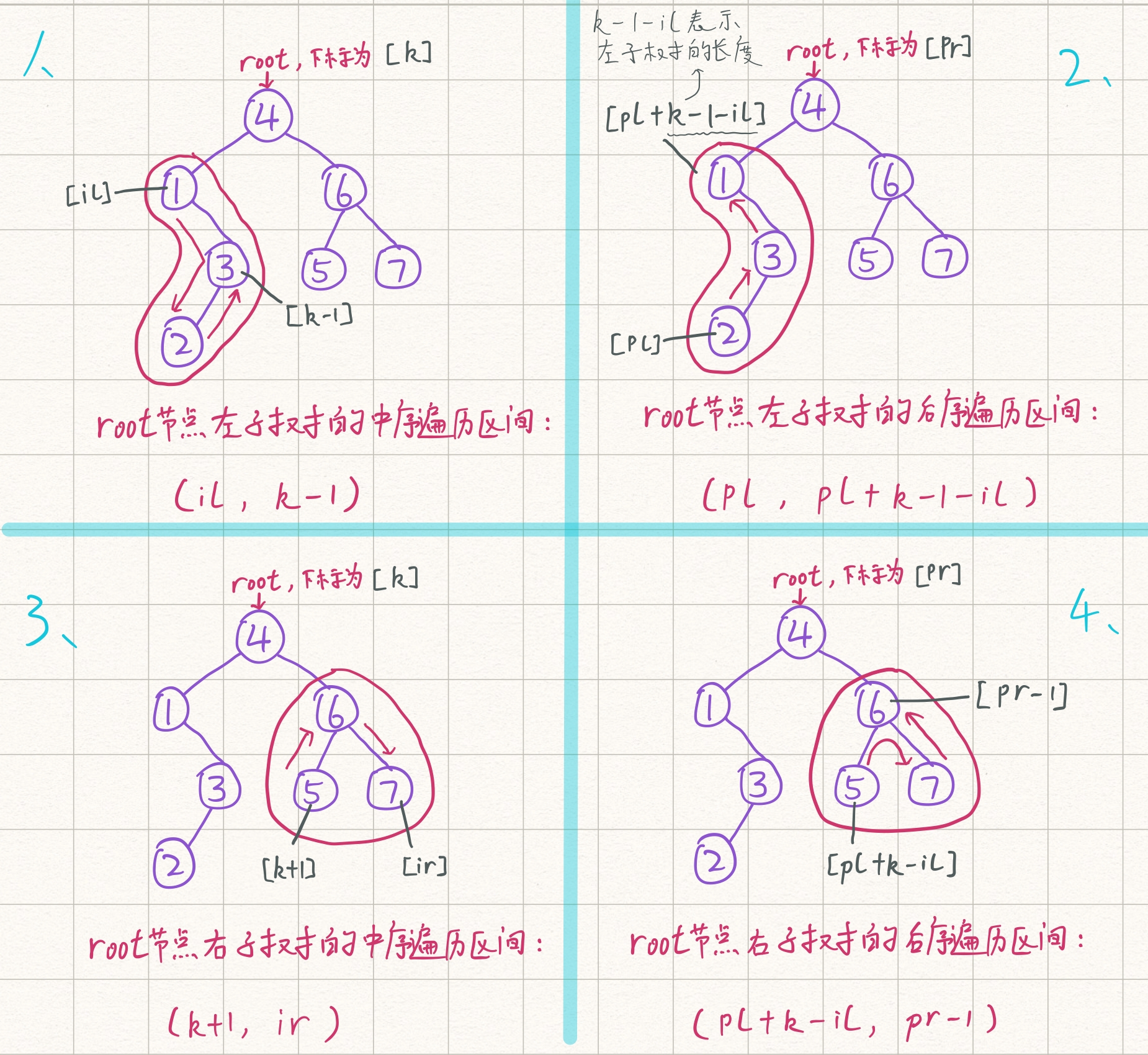
本题难点在于递归建树时,中序和后序遍历的区间选择,举例如下图:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
const int N = 40;
int n;
int postorder[N], inorder[N]; //前序遍历,中序遍历
unordered_map<int, int> l, r, pos; //用哈希表模拟二叉树
int build(int il, int ir, int pl, int pr)
{
int root = postorder[pr];
int k = pos[root]; //得到根节点在中序遍历中的下标
//k大于il表示根节点左边还有节点,即当前根节点存在左子树,下同
//下面两行是难点,举例解释见图
if (il < k) l[root] = build(il, k - 1, pl, pl + k - 1 - il);
if (ir > k) r[root] = build(k + 1, ir, pl + k - il, pr - 1);
return root;
}
void bfs(int root) //BFS用来层序遍历输出
{
queue<int> q;
q.push(root);
while (q.size())
{
auto t = q.front();
q.pop();
cout << t << ' ';
if (l.count(t)) q.push(l[t]); //判断该节点的左右儿子是否存在
if (r.count(t)) q.push(r[t]); //存在则加入队列,等待下一层遍历
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) cin >> postorder[i];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
{
cin >> inorder[i];
pos[inorder[i]] = i; //记录中序遍历每个点位置(剪枝)
}
int root = build(0, n - 1, 0, n - 1); //参数为中序遍历区间和后序遍历区间
bfs(root);
return 0;
}


很清晰呀!赞!
tql
请问一下,最后的输出格式:行首尾不得有多余空格。 需要怎么编写?(我在其他题目中遇到这个问题一直过不了)
if(变量!=行首尾变量 )cout<<” “;
std::cout << x << ” \n”[x == ans.back()];
写的非常的好,还是ipad更方便
第4张图的pr应该指在6上,对吗?
对对,感谢指正,已经修改了😘