




代码
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#define x first
#define y second
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int N = 25;
struct Node
{
int x, y, dir;
};
int n, m;
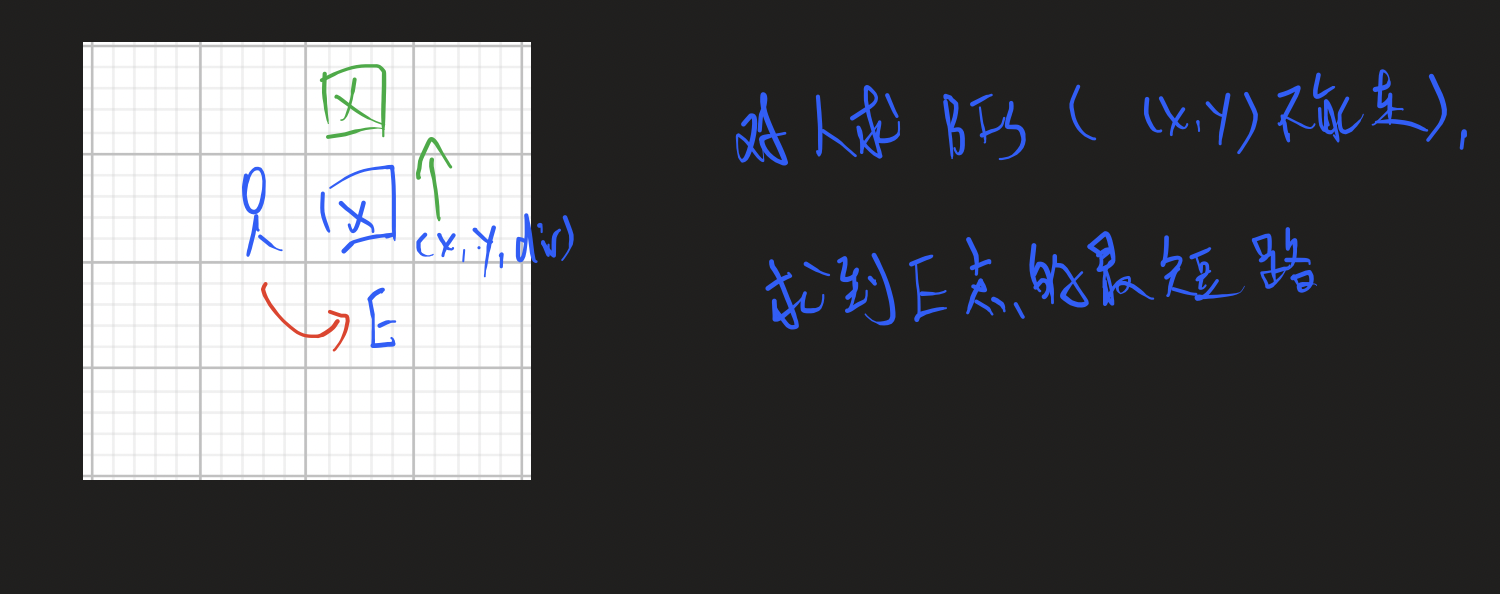
char g[N][N]; // 存储游戏地图
Node pre[N][N][4]; // 表示箱子在(x, y),上一个格子在i方向上的状态,即上一个状态是(x + dx[i], y + dy[i])
vector<int> path[N][N][4]; // path[j][k][i] 表示人从推(j,k,i)的上一个状态的位置,走到推(j,k,i)这个状态的位置的行走路径
bool st[N][N][4], used[N][N]; // BFS的判重数组,为了防止BFS遍历相同状态
PII dist[N][N][4]; // dist[j][k][i]是表示从初始状态到达j,k,i状态所需要的箱子最短路程和人行走最短路程
int dx[4] = {1, -1, 0, 0}, dy[4] = {0, 0, 1, -1}; // 依次表示下、上、右、左四个方向
int pre_man[N][N]; // pre_man[x][y]表示人从哪个方向走到(x, y),如果pre_man[x][y] = i, 那么上一个状态是(x - dx[i], y - dy[i])
bool check(int x, int y) // 判断(x, y)是否在地图内,且是空地
{
return x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < m && g[x][y] != '#';
}
void output(Node end, PII box)
{
char ops[] = "nswe";
string res;
while (end.dir != -1) {
res += ops[end.dir] - 32;
for (auto dir : path[end.x][end.y][end.dir])
res += ops[dir];
end = pre[end.x][end.y][end.dir];
printf("(%d,%d,%d) ", end.x, end.y, end.dir);
}
reverse(res.begin(), res.end());
cout << res << endl;
}
// 求人从start走到end,中间不经过box的最短路径,行走的序列保存到seq中
int bfs_man(PII start, PII end, PII box, vector<int>& seq)
{
memset(used, false, sizeof used);
memset(pre_man, -1, sizeof pre_man);
queue<PII> q;
q.push(start);
used[start.first][start.second] = true;
used[box.first][box.second] = true;
while (q.size()) {
auto t = q.front();
q.pop();
if (t == end) {
seq.clear();
int x = t.first, y = t.second;
while (pre_man[x][y] != -1) {
int dir = pre_man[x][y] ^ 1;
seq.push_back(dir);
x += dx[dir], y += dy[dir];
}
return seq.size();
}
for (int ii = 0; ii < 4; ii++) {
int i = ii ^ 1;
int x = t.first, y = t.second;
int a = x + dx[i], b = y + dy[i];
if (check(a, b) && !used[a][b]) {
used[a][b] = true;
pre_man[a][b] = i;
q.push({a, b});
}
}
}
return -1;
}
bool bfs_box(PII man, PII box, Node& end)
{
memset(st, false, sizeof st);
queue<Node> q;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int x = box.first, y = box.second;
int a = x + dx[i], b = y + dy[i];
int j = x - dx[i], k = y - dy[i];
vector<int> seq;
if (check(a, b) && check(j, k) && bfs_man(man, {a, b}, box, seq) != -1) {
st[j][k][i] = true;
q.push({j, k, i});
dist[j][k][i] = {1, seq.size()};
path[j][k][i] = seq;
pre[j][k][i] = {x, y, -1};
}
}
bool success = false;
PII man_d = {1e9, 1e9};
while (q.size()) {
auto t = q.front();
q.pop();
if (g[t.x][t.y] == 'T') {
success = true;
if (dist[t.x][t.y][t.dir] < man_d) {
man_d = dist[t.x][t.y][t.dir];
end = t;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int a = t.x + dx[i], b = t.y + dy[i];
int j = t.x - dx[i], k = t.y - dy[i];
if (check(a, b) && check(j, k)) {
vector<int> seq;
auto& p = dist[j][k][i];
int distance = bfs_man({t.x + dx[t.dir], t.y + dy[t.dir]}, {a, b}, {t.x, t.y}, seq);
if (distance != -1) {
PII td = {dist[t.x][t.y][t.dir].first + 1, dist[t.x][t.y][t.dir].second + distance};
if (!st[j][k][i]) {
st[j][k][i] = true;
q.push({j, k, i});
path[j][k][i] = seq;
pre[j][k][i] = t;
p = td;
}
else if (p > td) {
p = td;
path[j][k][i] = seq;
pre[j][k][i] = t;
}
}
}
}
}
return success;
}
int main()
{
int T = 1;
while (cin >> n >> m, n || m) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cin >> g[i];
printf("Maze #%d\n", T++);
PII man, box;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++)
if (g[i][j] == 'S')
man = {i, j};
else if (g[i][j] == 'B')
box = {i, j};
Node end;
if (!bfs_box(man, box, end))
puts("Impossible.");
else {
char ops[] = "nswe";
string res;
while (end.dir != -1) {
res += ops[end.dir] - 32;
for (auto dir : path[end.x][end.y][end.dir])
res += ops[dir];
end = pre[end.x][end.y][end.dir];
}
reverse(res.begin(), res.end());
cout << res << endl;
}
puts("");
}
return 0;
}

