<—点个赞吧QwQ
宣传一下算法提高课整理
已知有两个字串 A, B 及一组字串变换的规则(至多 6 个规则):
A1→B1
A2→B2
…
规则的含义为:在 A 中的子串 A1 可以变换为 B1、A2 可以变换为 B2…。
例如:A=abcd B=xyz
变换规则为:
abc → xu ud → y y → yz
则此时,A 可以经过一系列的变换变为 B,其变换的过程为:
abcd → xud → xy → xyz
共进行了三次变换,使得 A 变换为 B。
输入格式
输入格式如下:
A B
A1 B1
A2 B2
… …
第一行是两个给定的字符串 A 和 B。
接下来若干行,每行描述一组字串变换的规则。
所有字符串长度的上限为 20。
输出格式
若在 10 步(包含 10 步)以内能将 A 变换为 B ,则输出最少的变换步数;否则输出 NO ANSWER!。
输入样例:
abcd xyz
abc xu
ud y
y yz
输出样例:
3
思路
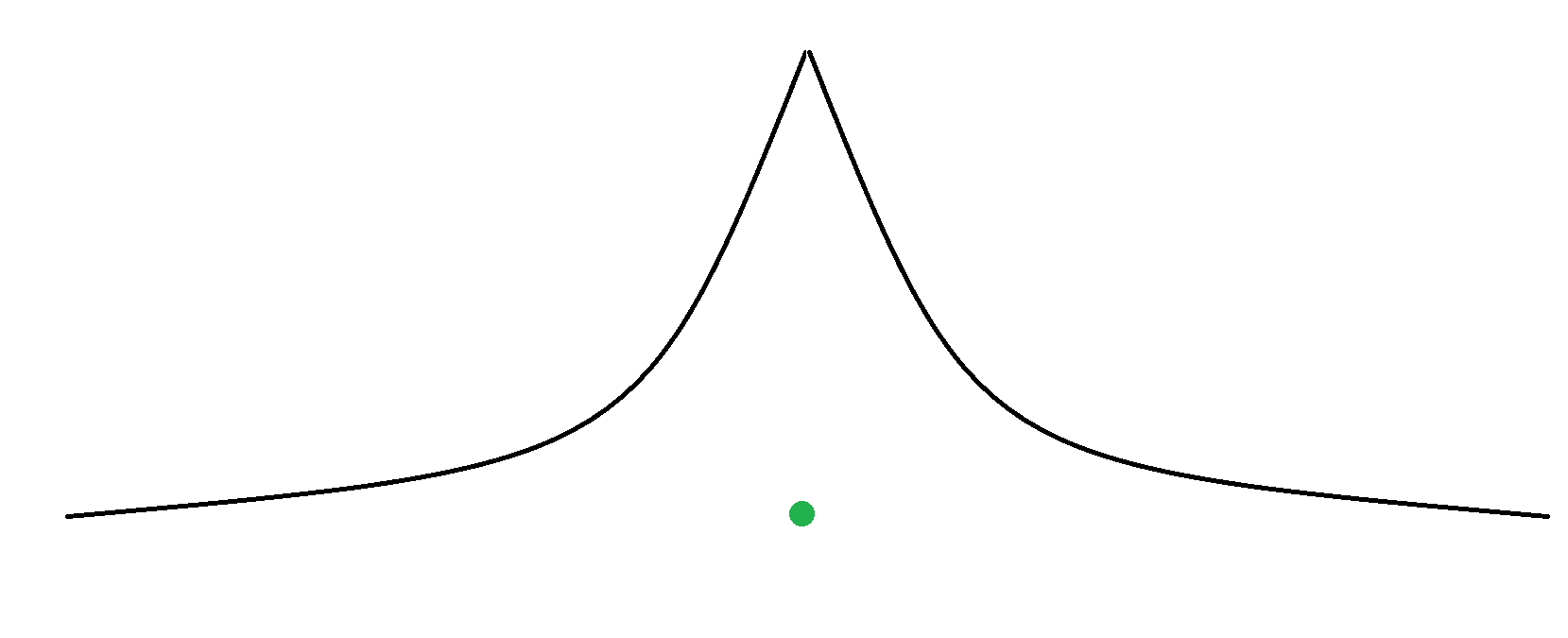
双向搜索,就是在起点搜索的过程,终点也在往回搜,从而达到优化的效果。
普通搜索:(绿色点为终点)
双向搜索:
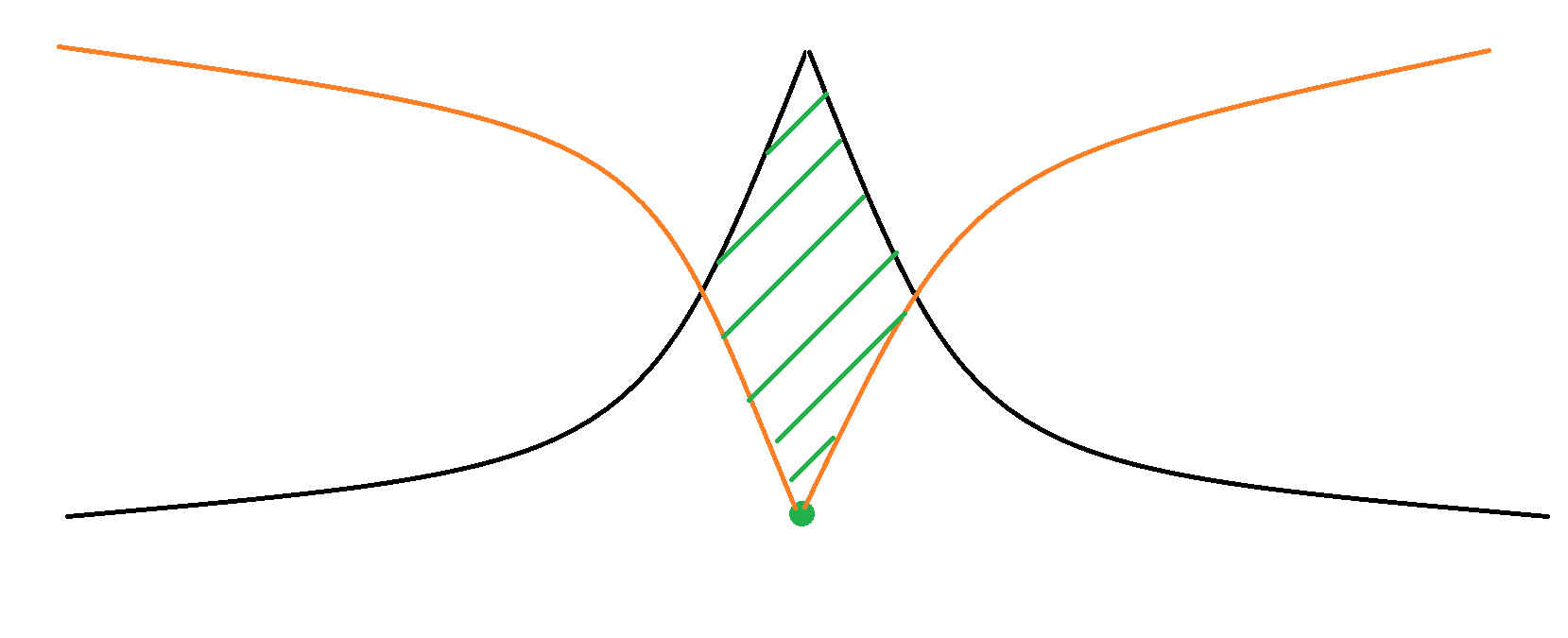
大家可以发现,双向搜索的大小非常小,所以已知起点和终点状态的搜索尽量用双向搜索。
具体可以看代码。
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
const int N = 10;
string A,B;
int n;
string a[N],b[N];
int extend (queue <string> &q,unordered_map <string,int> &da,unordered_map <string,int> &db,string a[],string b[]) {//每次扩展一层
string t = q.front ();
q.pop ();
for (int i = 0;i < t.size ();i++) {
for (int j = 0;j < n;j++) {
if (t.substr (i,a[j].size ()) == a[j]) {
string state = t.substr (0,i)+b[j]+t.substr (i+a[j].size ());
if (db.count (state)) return da[t]+1+db[state];
if (da.count (state)) continue;
da[state] = da[t]+1;
q.push (state);
}
}
}
return 11;
}
int bfs () {
queue <string> qa,qb;
unordered_map <string,int> da,db;
qa.push (A);
qb.push (B);
da[A] = 0;
db[B] = 0;
while (!qa.empty () && !qb.empty ()) {
int t;
if (qa.size () <= qb.size ()) t = extend (qa,da,db,a,b);
else t = extend (qb,db,da,b,a);
if (t <= 10) return t;
}
return 11;
}
int main () {
cin >> A >> B;
if (A == B) {
puts ("0");
return 0;
}
while (cin >> a[n] >> b[n]) n++;
int ans = bfs ();
if (ans > 10) puts ("NO ANSWER!");
else cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}


你好,我想问难道不是一层一层搜吗
两边一起往中间搜索
你好,我想问一个问题,假设从起点开始搜索时,A,B为两个状态,A->B通过的操作是C,那么从终点反向搜索B->A时的操作不应该是C的逆操作C’吗?为什么双向广搜从终点开始搜索用的操作还是C,不应该是C’吗?
的确,但是这里只需要求步数
b数组和a数组不是交换位置了吗?是说的这个嘛?
反向的时候是吧bi 变成ai比如 正着来是xyz>xu那么反向就是xu>xyz
你的代码wa了吗貌似数据加强了
加了等于10的特判
为什么把qa,qb和da,db写成全局变量然后不加引用符就错了哇
因为有时会交换da,db进行扩展,因为双向搜索时会翻着搜啊
还是没大懂┭┮﹏┭┮,还有一个问题就是y总不是说要一层一层搜吗,
while(da[q.front()]==d&&q.size())这样就会Segmentation Fault
但是交换一下顺序就不会了不知道为什么
而且如果我设成了全局变量那个extend函数里用的一定也是对的呀,当拓展a时,用的就是qa,然后依次是da,db,我没看出来哪里有错呀,大佬能看一下具体代码是哪行影响的嘛
因为C++的判断语句如果第一个数是0,那么后面的语句就不执行了
因为C++的判断语句如果第一个数是0,那么后面的语句就不执行了
你发一个代码给我看看
#include <iostream> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> #include <queue> #include <unordered_map> using namespace std; const int N = 6; int n; string A, B; string a[N], b[N]; int extend(queue<string>& q, unordered_map<string, int>&da, unordered_map<string, int>& db, string a[N], string b[N]) { int d = da[q.front()]; while (da[q.front()] == d &&q.size()) { auto t = q.front(); q.pop(); for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) for (int j = 0; j < t.size(); j ++ ) if (t.substr(j, a[i].size()) == a[i]) { string r = t.substr(0, j) + b[i] + t.substr(j + a[i].size()); if (db.count(r)) return da[t] + db[r] + 1; if (da.count(r)) continue; da[r] = da[t] + 1; q.push(r); } } return 11; } int bfs() { if (A == B) return 0; queue<string> qa, qb; unordered_map<string, int> da, db; qa.push(A), qb.push(B); da[A] = db[B] = 0; int step = 0; while (qa.size() && qb.size()) { int t; if (qa.size() < qb.size()) t = extend(qa, da, db, a, b); else t = extend(qb, db, da, b, a); if (t <= 10) return t; if ( ++ step == 10) return -1; } return -1; } int main() { cin >> A >> B; while (cin >> a[n] >> b[n]) n ++ ; int t = bfs(); if (t == -1) puts("NO ANSWER!"); else cout << t << endl; return 0; }这是y总代码就改了个顺序就不行了,很好奇
对呀,就反一个方向扩展
q.size()要放前面
q.size()放前面后面有啥区别呀
因为C++的判断语句&的特性,如果不懂,你看下CSP-J T3:如果第一个数是0,那么后面的语句就不执行了
这个我会了,但是那个&符还是不清楚为什么全局变量不行qwq
那个是引用hh
就是为了把在函数内修改后的参数也同时把函数为的调用变量修改了
举个例子:
比如:
void swap (int a,int b){ int t = a; a = b; b = t; }是不能交换两个数的。
而
void swap (int &a,int &b){ int t = a; a = b; b = t; }就可以