以下内容总结自:
徐隆曦 - Java 并发编程 78 讲 - [9]Future 掌控未来
Callable与Runnable接口的区别?
可以从三个角度进行分析:
第一,方法名
Callable接口规定的执行方法是call(),
而Runnable接口规定的执行方法是run()。
第二,返回值
Callable接口的任务执行后有返回值,而Runnable没有。
第三,抛出异常
call()方法可以抛出checked exception,而run()不能。
Future接口的作用是什么?
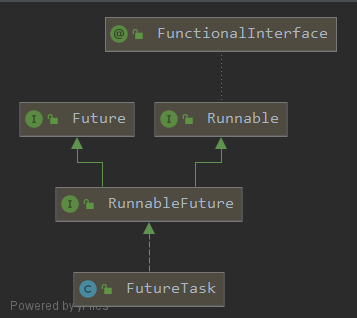
Future首先是一个接口,它包含get()、cancel()、isDone()等方法。
而FutureTask是一个工具类,它实现了RunnableFuture接口,而RunnableFuture接口继承了Runnable和Future接口。
来看下关系图:
让我们看下get()方法的用法:
public class CallableGetTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Callable<Integer> ctask = () -> {
Thread.sleep(3000);
// int a = 10 / 0; // ExecutionException
return new Random().nextInt();
};
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
Future<Integer> future = service.submit(ctask);
try {
service.shutdownNow(); // InterruptedException
future.get(4, TimeUnit.SECONDS); // TimeoutException
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException | TimeoutException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
service.shutdown();
}
}
可以看到,你需要注意三种异常情况:
InterruptedException: 调用get()方法时,任意已被中断。ExecutionException: 执行任务时,发生执行异常。TimeoutException: 超过设置的超时时间,但是该任务还没执行完成。
那么使用Future接口时需要注意什么?
第一,批量获取Future结果时,容易发生Block,因此get()方法应该使用timeout限制。
第二,Future的生命周期不能逆,一旦完成了任务,那么状态就永久停在"已完成"。
使用Future时是否产生了新的线程?
并没有。
因为Runnable和Future本身并不能产生新的线程,
它们需要借助其他方式,如构建Thread类,或使用线程池才能执行任务。
CompletableFuture类的作用是什么?
来看个例子:
假如,我需要实现这样一个功能:分别查询三家航空公司,从北京到上海的机票价格。
不同航空公司的接口响应时间肯定不同,并且我们也不能一直等待响应结果,
所以设置阈值为3秒,代表仅显示三秒内返回的数据。
使用线程池实现
public class TourismUsingThreadPool {
private ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
long s = System.currentTimeMillis();
TourismUsingThreadPool demo1 = new TourismUsingThreadPool();
Set<Integer> prices = demo1.getPrices();
System.out.println(prices);
long e = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("Cost " + (e - s) + "ms");
}
private Set<Integer> getPrices() throws InterruptedException {
Set<Integer> prices = Collections.synchronizedSet(new HashSet<Integer>());
service.submit(new Task("Shanghai", prices));
service.submit(new Task("Shanghai", prices));
service.submit(new Task("Shanghai", prices));
Thread.sleep(3000);
service.shutdown();
return prices;
}
private class Task implements Runnable{
private String destination;
private Set<Integer> prices;
private Task(String destination, Set<Integer> prices) {
this.destination = destination;
this.prices = prices;
}
@Override
public void run() {
int price = 0;
try {
Thread.sleep((long) (Math.random() * 4000));
price = (int) (Math.random() * 4000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
prices.add(price);
}
}
}
以下是一种返回结果:
[596, 1807]
Cost 3003ms
你有没有发现,我们可以做一些优化,
举个例子,如果三家航空公司都在3秒内返回数据,那么我们就可以提前返回结果。
所以,我们可以用CountDownLatch:
使用CountDownLatch实现
public class TourismUsingCountDownLatch {
private ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
long s = System.currentTimeMillis();
TourismUsingCountDownLatch tourism = new TourismUsingCountDownLatch();
Set<Integer> prices = tourism.getPrices();
System.out.println(prices);
long e = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("Cost " + (e - s) + "ms");
}
private Set<Integer> getPrices() throws InterruptedException {
Set<Integer> prices = Collections.synchronizedSet(new HashSet<Integer>());
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(3);
service.submit(new Task("Shanghai", prices, latch));
service.submit(new Task("Shanghai", prices, latch));
service.submit(new Task("Shanghai", prices, latch));
latch.await(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
service.shutdown();
return prices;
}
private class Task implements Runnable{
private String dest;
private Set<Integer> prices;
private CountDownLatch latch;
private Task(String dest, Set<Integer> prices, CountDownLatch latch) {
this.dest = dest;
this.prices = prices;
this.latch = latch;
}
@Override
public void run() {
int price = 0;
try {
Thread.sleep((long) (Math.random() * 400));
price = (int) (Math.random() * 400);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
prices.add(price);
latch.countDown();
}
}
}
来看下其中一种结果:
[369, 263, 329]
Cost 378ms
使用CompletableFuture实现
再来看下使用CompletableFuture的实现方式:
public class TourismUsingCompletableTask {
public static void main(String[] args) {
long s = System.currentTimeMillis();
TourismUsingCompletableTask tourism = new TourismUsingCompletableTask();
Set<Integer> prices = tourism.getPrices();
System.out.println(prices);
long e = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("Cost " + (e - s) + "ms");
}
private Set<Integer> getPrices() {
Set<Integer> prices = Collections.synchronizedSet(new HashSet<>());
CompletableFuture<Void> task1 = CompletableFuture.runAsync(new Task("Shanghai", prices));
CompletableFuture<Void> task2 = CompletableFuture.runAsync(new Task("Shanghai", prices));
CompletableFuture<Void> task3 = CompletableFuture.runAsync(new Task("Shanghai", prices));
CompletableFuture<Void> allTasks = CompletableFuture.allOf(task1, task2, task3);
try {
allTasks.get(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException | TimeoutException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return prices;
}
private class Task implements Runnable{
private String dest;
private Set<Integer> prices;
private Task(String dest, Set<Integer> prices) {
this.dest = dest;
this.prices = prices;
}
@Override
public void run() {
int price = 0;
try {
Thread.sleep((long) (Math.random() * 400));
price = (int) (Math.random() * 400);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
prices.add(price);
}
}
}
来看下其中一种结果:
[240, 212, 191]
Cost 260ms

