PAT甲级-2021春季题解
前些天找了一套pat甲级的题目练手,虽然作答时间几乎用完代码写的也不太体面,但还是放个题解记录一下。以上
7-1 Arithmetic Progression of Primes
分数 20
作者 陈越
单位 浙江大学
In mathematics, an arithmetic progression (AP,等差数列) is a sequence of numbers such that the difference between the consecutive terms is constant. In 2004, Terence Tao (陶哲轩) and Ben Green proved that for any positive n, there exists at least one arithmetic progression consists of n consecutive prime numbers. For example, { 7,37,67,97,127,157 } is one solution for n=6. Now it is your job to find a maximum solution for a given n within a given range.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case, which gives two positive integers in a line: n (≤10), the number of consecutive prime terms in an arithmetic progression, and MAXP (2≤MAXP<105), the upper bound of the largest prime in the solution.
Output Specification:
For each test case, if there exists a solution, print in ascending order the prime numbers in a line. If the solution is not unique, output the one with the maximum common difference. If there is still a tie, print the one with the maximum first number. If there is no solution bounded by MAXP, output the largest prime in the given range instead.
All the numbers in a line must be separated by a space, and there must be no extra space at the beginning or the end of the line.
Sample Input 1:
5 1000
Sample Output 1:
23 263 503 743 983
Sample Input 2:
10 200
Sample Output 2:
199
代码长度限制 16 KB
时间限制 1000 ms
内存限制 64 MB
理论上应该是送分题但自己憨批了,卡了好久,真的卡了好久……(通过率14.22在四道题中倒数第一的签到题你喜欢吗)
可以拆成两个环节,生成质数表和在给定数列(前面的质数标)按照要求“抠”出一个等差出列
当时没想到在给定最大值和数列长度的情况下可以直接算出最大间距(这部分可以看 https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44997802/article/details/119948021 这篇题解中给出的方法),采用的起始点从大到小,间距从小到大一路暴力的方案,好在时间要求比较松360ms过了
感觉还能优化,但是我懒了
// 7-1 Arithmetic Progression of Primes (20)
// 2022/05/21 15:03:04 暴力360ms
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
#define N 100010
bool notprime[N] = {1, 1, 0};
vector<int> prime, seq;
int maxstep = -1;
void init(int maxp) {
for (int i = 2; i <= maxp; i++) {
if (!notprime[i])
prime.push_back(i);
for (int j = 2; j * i <= maxp; j++)
notprime[i * j] = 1;
}
}
// 防止直接访问notPrime进行判断的时候指向下标为负
inline bool isPrime(int i) {
return (i <= 0 ? 0 : (!notprime[i]));
}
// 检查从start往前按step间距能否找到长为len的合法数组
bool check(int start, int step, int len) {
static vector<int> tmpseq(len);
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
if (isPrime(start - i * step))
tmpseq[i] = start - i * step;
else
return false;
if (step > maxstep) {
maxstep = step;
seq.swap(tmpseq);
}
return true;
}
int main() {
int n, maxp;
scanf("%d%d", &n, &maxp);
init(maxp);
// solve
seq.resize(n, 0);
bool flag = 0;
for (int i = prime.size() - 1; i > 0; i--) {
for (int j = i - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
flag = check(prime[i], prime[i] - prime[j], n);
}
}
if (maxstep == -1)
printf("%d\n", prime.back());
else {
reverse(seq.begin(), seq.end());
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("%d%c", seq[i], (i == n - 1 ? '\n' : ' '));
}
return 0;
}
7-2 Lab Access Scheduling
分数 25
作者 陈翔
单位 浙江大学
Nowadays, we have to keep a safe social distance to stop the spread of virus due to the COVID-19 outbreak. Consequently, the access to a national lab is highly restricted. Everyone has to submit a request for lab use in advance and is only allowed to enter after the request has been approved. Now given all the personal requests for the next day, you are supposed to make a feasible plan with the maximum possible number of requests approved. It is required that at most one person can stay in the lab at any particular time.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. Each case starts with a positive integer N (≤2×103), the number of lab access requests. Then N lines follow, each gives a request in the format:
hh:mm:ss hh:mm:ss
where hh:mm:ss represents the time point in a day by hour:minute:second, with the earliest time being 00:00:00 and the latest 23:59:59. For each request, the two time points are the requested entrance and exit time, respectively. It is guaranteed that the exit time is after the entrance time.
Note that all times will be within a single day. Times are recorded using a 24-hour clock.
Output Specification:
The output is supposed to give the total number of requests approved in your plan.
Sample Input:
7
18:00:01 23:07:01
04:09:59 11:30:08
11:35:50 13:00:00
23:45:00 23:55:50
13:00:00 17:11:22
06:30:50 11:42:01
17:30:00 23:50:00
Sample Output:
5
Hint:
All the requests can be approved except the last two.
代码长度限制 16 KB
时间限制 200 ms
内存限制 64 MB
区间贪心?线段不相交问题?应该算是,不难(通过率32.57)
把指定格式时间转换成秒为单位的时间戳,按结束时间排个序就可以处理了
同一秒允许同时发生离开和进入(可以参考样例)
// 7-2 Lab Access Scheduling (25)
// 2022/05/21 15:21:21 4ms
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
const int end_of_day = 23 * 3600 + 59 * 60 + 59;
struct p {
int beg, end;
};
inline int cov(int &h, int &m, int &s) {
return (s + m * 60 + h * 60 * 60);
}
bool cmp(const p &a, const p &b) { return a.end < b.end; }
int main() {
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
vector<p> ls(n);
int bh, bm, bs, eh, em, es;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
scanf("%d:%d:%d %d:%d:%d", &bh, &bm, &bs, &eh, &em, &es);
ls[i] = {cov(bh, bm, bs), cov(eh, em, es)};
}
sort(ls.begin(), ls.end(), cmp);
vector<p> seq;
int t = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < ls.size(); i++) {
if (ls[i].beg >= t && ls[i].end <= end_of_day) {
seq.push_back(ls[i]);
t = ls[i].end;
}
}
printf("%d", seq.size());
return 0;
}
7-3 Structure of Max-Heap
分数 25
作者 陈越
单位 浙江大学
In computer science, a max-heap is a specialized tree-based data structure that satisfies the heap property: if P is a parent node of C, then the key (the value) of P is greater than or equal to the key of C. A common implementation of a heap is the binary heap, in which the tree is a complete binary tree.
Your job is to first insert a given sequence of integers into an initially empty max-heap, then to judge if a given description of the resulting heap structure is correct or not. There are 5 different kinds of description statements:
x is the rootx and y are siblingsx is the parent of yx is the left child of yx is the right child of y
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line gives 2 positive integers: N (≤1,000), the number of keys to be inserted, and M (≤20), the number of statements to be judged. Then the next line contains N distinct integer keys in [−104,104] which are supposed to be inserted into an initially empty max-heap. Finally there are M lines of statements, each occupies a line.
Output Specification:
For each statement, print 1 if it is true, or 0 if not. All the answers must be print in one line, without any space.
Sample Input:
5 6
23 46 26 35 88
35 is the root
46 and 26 are siblings
88 is the parent of 46
35 is the left child of 26
35 is the right child of 46
-1 is the root
Sample Output:
011010
代码长度限制 16 KB
时间限制 400 ms
内存限制 64 MB
没啥好说的,手写大根堆就行,倒是那个输入处理有点烦人……自己用了一个eat函数来吃掉单词处理的(也在别的题解看到了巨大量sscanf的方案……更头疼了啊……),感觉不太体面。看了别人的题解发现可以用map存储数值对应的位置下标,当时没想到有点遗憾
代码长度有点超标但用时6ms,还算体面(通过率25.92)
// 7-3 Structure of Max-Heap (25)
// 2022/05/21 16:18:06 6ms
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
vector<int> heap;
int heap_size;
void build_heap();
void eat(int n);
int heap_find(int val) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < heap_size; i++)
if (heap[i] == val) break;
if (heap[i] == val)
return i;
else
return -1;
}
int parent(int son_val) {
int i = heap_find(son_val);
if (i > 0) //排除根和没找到
return (i - 1) / 2;
else
return -1;
}
int main() {
int req_num;
cin >> heap_size >> req_num;
build_heap();
while (req_num--) {
int x, y;
string s;
cin >> x >> s;
if (s == "and") {
cin >> y;
int px = parent(x), py = parent(y);
cout << (px == py && px >= 0 && py >= 0);
eat(2);
} else {
eat(1);
cin >> s;
if (s == "root") {
cout << (heap[0] == x);
} else if (s == "parent") {
eat(1);
cin >> y;
int pos_x = heap_find(x), par_y = parent(y);
cout << (pos_x == par_y && pos_x >= 0);
} else if (s == "left") {
eat(2);
cin >> y;
int pos_x = heap_find(x), pos_y = heap_find(y);
cout << (pos_y >= 0 && pos_x == (2 * pos_y + 1));
} else { // right_child
eat(2);
cin >> y;
int pos_x = heap_find(x), pos_y = heap_find(y);
cout << (pos_y >= 0 && pos_x == (2 * pos_y + 2));
}
}
}
return 0;
}
void up(int son, int lim);
// void down();
void build_heap() {
heap.resize(heap_size);
for (int i = 0; i < heap_size; i++) {
cin >> heap[i];
up(i, i);
}
}
void up(int son, int lim) {
while (son) {
int p = (son - 1) / 2;
if (heap[son] > heap[p])
swap(heap[son], heap[p]);
else
break;
son = p;
}
}
void eat(int n) {
string s;
while (n--) cin >> s;
}
7-4 Recycling of Shared Bicycles
分数 30
作者 陈越
单位 浙江大学
There are many spots for parking the shared bicycles in Hangzhou. When some of the bicycles are broken, the management center will receive a message for sending a truck to collect them. Now given the map of city, you are supposed to program the collecting route for the truck. The strategy is a simple greedy method: the truck will always move to the nearest spot to collect the broken bicycles. If there are more than one nearest spot, take the one with the smallest index.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains two positive integers: N (≤ 200), the number of spots (hence the spots are numbered from 1 to N, and the management center is always numbered 0), and M, the number of streets connecting those spots. Then M lines follow, describing the streets in the format:
S1 S2 Dist
where S1 and S2 are the spots at the two ends of a street, and Dist is the distance between them, which is a positive integer no more than 1000. It is guaranteed that each street is given once and S1 is never the same as S2.
Output Specification:
For each case, first print in a line the sequence of spots in the visiting order, starting from 0. If it is impossible to collect all the broken bicycles, output in the second line those spots that cannot be visited, in ascending order of their indices. Or if the job can be done perfectly, print in the second line the total moving distance of the truck.
All the numbers in a line must be separated by 1 space, and there must be no extra space at the beginning or the end of the line.
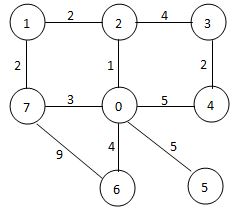
Sample Input 1 (shown by the figure below):
7 10
0 2 1
0 4 5
0 7 3
0 6 4
0 5 5
1 2 2
1 7 2
2 3 4
3 4 2
6 7 9
Sample Output 1:
0 2 1 7 6 3 4 5
33
Sample Input 2:
7 8
0 2 1
0 4 5
0 7 3
1 2 2
1 7 2
2 3 4
3 4 2
6 5 1
Sample Output 2:
0 2 1 7 3 4
5 6
代码长度限制 16 KB
时间限制 200 ms
内存限制 64 MB
想了想应该是多源最短路,节点数量也不多直接上floyd了。第一次手写图的算法题。
四个题里面通过率最高(35.53)
// 7-4 Recycling of Shared Bicycles (30)
// 2022/05/21 17:05:54 20ms
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
#define N 210
const int INF = 1e9 + 7;
int g[N][N], n, node_cnt, dis_cnt;
bool visited[N];
vector<int> seq;
void init();
void floyd();
void greedy();
int main() {
int m;
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
init();
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int a, b, dis;
scanf("%d %d %d", &a, &b, &dis);
g[a][b] = g[b][a] = dis;
}
floyd();
greedy();
for (int i = 0; i < node_cnt; i++)
printf("%d%c", seq[i], (i == node_cnt - 1 ? '\n' : ' '));
if (node_cnt == n + 1)
printf("%d", dis_cnt);
else {
int space = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if (!visited[i])
printf("%s%d", ((space++) ? " " : ""), i);
}
return 0;
}
void init() {
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 0; j <= n; j++)
g[i][j] = (i == j) ? 0 : INF;
}
void floyd() {
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
for (int l = 0; l <= n; l++)
for (int r = 0; r <= n; r++)
if (g[l][i] != INF && g[i][r] != INF && (g[l][r] > g[l][i] + g[i][r]))
g[l][r] = g[l][i] + g[i][r];
}
void greedy() {
int q[N] = {0}, l = 0, r = 1;
while (l != r) {
int curr = q[l++], dis = INF, next = 0;
visited[curr] = true;
seq.push_back(curr);
node_cnt++;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if (visited[i] == false && g[curr][i] < dis)
next = i, dis = g[curr][i];
if (next) {
dis_cnt += dis;
q[r++] = next;
}
}
}
私货时间:练习的代码扔到gitee上了(包括本篇题解),欢迎批评/指正/建议/取用嘛现在一个star都没有就是了